|
Article Index
Africa is the worlds second largest continent, it contains 23% of the worlds land.
13% of the worlds population is in Africa. Africa lies on part of the
equator, and is mostly located in the tropics. The west side of Africa is bordered
by the Atlantic Ocean, the east side is bordered by the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea, and the north is bordered by the Mediterranean
Sea and is connected to Asia by the small Sinai Peninsula.
Africa is A Land of Diversity, if you were to explore Africa you would pass lush rainforests, vast grassy plains, barren and dry deserts, tall mountains,
and find some of the mightiest rivers on earth. You would meet diverse peoples and hear hundreds of languages. There would be many cultures and backgrounds. You would pass
through small villages where daily life is the same has it was almost 100 years ago, untouched by much technology! But you would also pass through sprawling cities with tall skyscrapers, modern economies, and many international
cultural influences.
Africa is said to be the birthplace of the human race. Here it is said
that the human race evolved between 8 million and 5 million years ago. Modern
humans are said to have evolved between 130,000 and 90,000 years ago, and subsequently spread out of Africa. Ancient Egypt, one of the worlds first great civilizations, arose in northeast Africa more than 5,000 years
ago. Over the time many cultures and states rose and fell. But by 500 years ago there was many markets, prosperous cities, and centers of learning scattered across
the continent.
During
the last 500 years European traders came to Africa to conquer and observe. BUT
many Europeans took millions of Africans has slaves to work in Europe and eventually the United States of America (which of
course lead to a civil war). Europeans also tried to take part in the wealth
of raw materials in Africa to fuel their industries. In the late 19th century,
Europeans seized control and colonized almost all of Africa.
Through
slow reform or by violent struggle, most of Africa won its independence back in the 1950s and 1960s. Independent Africa inherited from colonization a weak position in todays global economy, underdeveloped
communication and transportation systems, and agreed political and geographical land boundaries. The citizens of these nations have little history or culture to bind them together. Which is creating much unrest on and in the continent. Civil
wars somewhere in Africa are almost a daily occurrence.
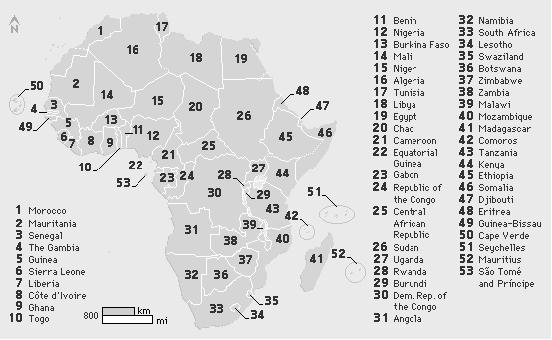
There
are 53 different African countries, including the 47 nations of the mainland and the 6 surrounding island nations. The continent
is commonly divided along the lines of the Sahara, the worlds largest desert, which cuts a huge swath through the northern
half of the continent. The countries north of the Sahara make up the region of North Africa, while the region south of the
desert is known as sub-Saharan Africa. Sub-Saharan Africa is sometimes referred to as Black Africa, but this designation is
not very helpful, given the ethnic diversity of the entire continent. North Africa consists of the countries of Algeria, Egypt,
Libya, Morocco, Sudan, and Tunisia. Sub-Saharan Africa is generally subdivided into the regions of West Africa, East Africa,
Central Africa, and southern Africa. For the purposes of this article, West Africa consists of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon,
Chad, Côte dIvoire, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, The Gambia,
and Togo. East Africa consists of Burundi, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Rwanda, Somalia, Tanzania,
and Uganda. Central Africa consists of Angola, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea,
Gabon, Republic of the Congo, and Zambia. Southern Africa consists of Botswana, Lesotho, Namibia, South Africa, Swaziland,
and Zimbabwe. The island nations located off the coast of Africa are Cape Verde and São Tomé and Príncipe in the Atlantic
Ocean; and Comoros, Madagascar, Mauritius, and Seychelles in the Indian Ocean.
The great diversity of Africas natural environment makes it hard to generalize.
Much of the continent is made up of vast plains with little rain or temperature relief, but there is also towering volcanoes, cool mountain tops,
and the largest rift valley system in the world. There is a lot of hot, dry,
and humid weather. But there is also cool, moist, and wet areas. Some of these areas can even support glaciers. It contains
regions of biological significance due to their biodiversity and huge numbers of species found nowhere else. (MSN Encarta®
Quote.)
The environment of Africa has been, for a long time, mistaken as a hostile, foreboding, and tragically decline. A popular description of Africa is the dark continent.
Nature Magazines shows untamed wilderness, and many disasters of droughts and famine for a look of Africa. Geographers accounts of Africa also used to make Africa more unattractive with its unfavorable environmentits
oppressive climate, infertile soil, polluted waters, and exotic diseases.
In the current days, Africa is getting a better outlook of its environment. We
are understanding more about Africas environment, and it is helping to unravel the past misconceptions. The relationships
of African societies with the environment is also much better understood than it was in the past. But much has to be done before most people will and can appreciate Africas environment, especially by the
general public.
The continent of Africa expands over 30 million square kilometers including its adjacent islands. It stretches 8,000 kilometers
from the northern most point to the southern most point of the continent. The
maximum width
of the continent is 7,500 kilometers. The highest point on the continent of Africa
is Mount Kilimanjaro, which is 5,895 meters tall or 19,341 feet tall. The lowest point in Africa is Lake Asal in Djibouti. Lake Asal is 153 meters below sea level or 502 feet below sea level.
Africa is surrounded by oceans and seas: the Atlantic Ocean on the west, the Indian Ocean on the east, the Red Sea
on the northeast, and the Mediterranean Sea on the north. Madagascar, the fourth largest island in the world, lies off the
southeastern coast. Other offshore islands include the Madeira Islands, Canary Islands, Cape Verde Islands, São Tomé, Príncipe,
and Bioko, off the western coast; and the Comoros Islands, Seychelles, Mascarene Islands, and Socotra, off the eastern coast.
(MSN Encarta® Quote)
Africa generally consists of a series of flat and gently undulating plateaus occurring at different levels, broken
by a few mountainous areas and by the rift valleys of East Africa. With a mean elevation of approximately 650 m (2,100 ft)
above sea level, Africa is high compared to other continents. The southern and eastern section of the continent, often called
High Africa, consists primarily of a high plateau with elevations between 1,000 and 2,000 m (3,000 and 7,000 ft) above sea
level. Northern and western Africa, widely known as Low Africa, has much lower mean elevations. Most of the continents surface
has been warped into a series of large, saucer-like basins separated by highlands. The major basins of Africa are El Djouf,
now occupied by the Niger River Basin in West Africa; the Chad Basin, surrounding Lake Chad in west central Africa; the Sudan
(or Nile River) Basin in northeast Africa; the Congo River Basin of Central Africa; and the Kalahari (or Okavango) Basin of
southern Africa. (MSN Encarta® Quote.)
The highest elevations in Africa are found mainly in the east. Kilimanjaro
is the tallest peak. Mount Kenya is the second tallest peak (5,199 m or 17,057 ft) found north of Mt. Kilimanjaro in central
Kenya. The third tallest mountain is Margherita Peak (5,109 m or 16,762 ft). Margherita Peak is found in the Ruwenzori Range
on the border of Uganda and the Democratic Republic of Congo. Ras Dashen is the
fourth tallest mountain (4,620 m or 15,157 ft) is found in the Ethiopian Highlands of northern Ethiopia. The fifth tallest mountain in Africa is Mount Meru (4,565 m or 14,977 ft) is close to Mt, Kilimanjaro in
Tanzania. The sixth tallest mountain in Africa is Mount Elgon (4,321 m or 14,177 ft) on the Uganda-Kenya border.
There are other mountainous regions besides in East Africa and West Central Africa.
These mountainous regions are on the northern and southern fringes of the continent.
The Atlas Mountains found in the north cross 2,200 kilometers (1,400 miles) from Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. The
Atlas Mountains is sort of parallel to the northern coast. These ranges enclose
a number of broad inland basins and plateaus. In the west, the High (or Grand) Atlas contains Toubkal (4,165 m/ 13,665 ft),
the highest peak of the system. Toward the east, the Atlas consists of two parallel ranges: the Tell Atlas to the north and
the Saharan Atlas to the south (MSN Encarta® Quote.)
Southern Africa has the Great Escarpment, which extends a total of 5,000 kilometers (3,000 miles) along the coast of
Angola to Mozambique. If you dont know what an escarpment is, it is a ridge the
is steep on one side and slopes down gently on the other side (sort of like a mountain cut in half down the middle). There is also the Drakensberg Mountains form the clearest form of relief from the
Great Escarpment. The Drakensberg Mountains rise up to 3,482 m (11,424 ft) at
Thabana Ntlenyana in Lesotho.
Cameroon Mountain is the highest peak in West Africa at 4,095 m (13,435 ft). To the north, isolated highlands occur
in the desert land of the Sahara, including the Ahaggar Mountains in southern Algeria and the Tibesti in northern Chad. (MSN
Encarta® Quote.)
Continued on the next page.
|
